[ad_1]
Featured SpeakerAlex Thorn
Head of Firmwide AnalysisGalaxy

Hear Alex Thorn share his tackle “Bitcoin and Inflation: It’s Sophisticated” at Consensus 2023.
The world’s main central banks seem to have stopped shrinking their stability sheets, a tactic they adopted final yr to manage inflation in a program that destabilized threat belongings, together with cryptocurrencies.
The so-called quantitative tightening ended lately and the cumulative stability sheet of main central banks – the U.S. Federal Reserve (Fed), European Central Financial institution (ECB), Financial institution of England (BOE) and Financial institution of Japan (BOJ) – has troughed, in keeping with information tracked by macroeconomic analysis agency TS Lombard and sourced from The Market Ear publication.
“The ‘delta of the delta’ has reversed these days. Attainable tailwind for markets,” Thursday’s version of The Market Ear stated, referring to the dip within the dimension of the banks’ stability sheets.
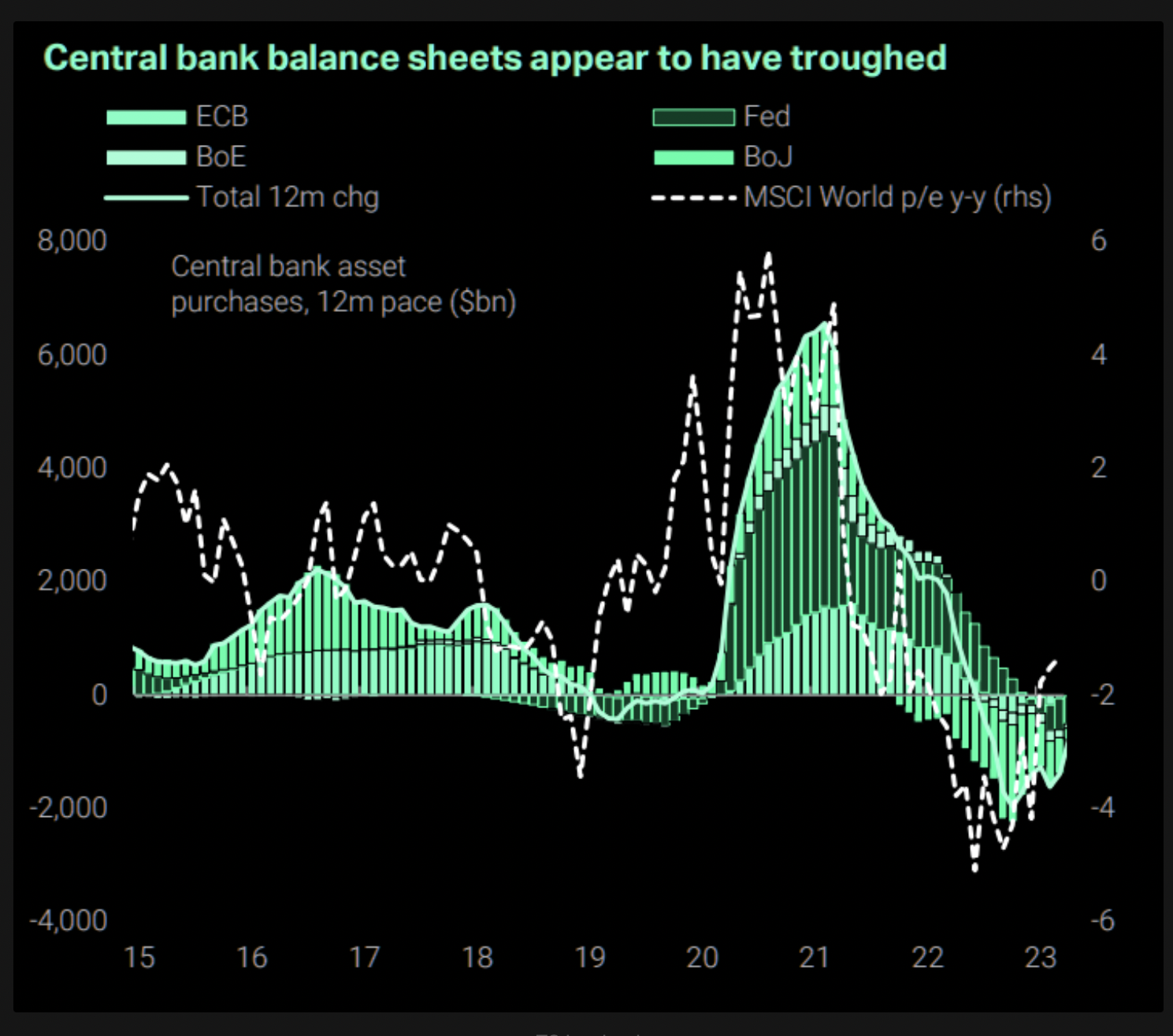
Central financial institution stability sheets seem to have troughed. (TS Lombard, The Market Ear) (TS Lombard, The Market Ear)
Enlargement of central banks’ stability sheets is extensively thought of bullish for threat belongings, together with bitcoin.
That’s as a result of entities concerned in monetary markets are sometimes the first recipients of the cash newly created by means of stability sheet enlargement, in keeping with a concept proposed by 18th-century Irish-French economist Richard Cantillon. These entities use the cash acquired to drive asset costs greater.
The jury continues to be out on whether or not the Fed’s current extension of loans to native lenders will consequence in contemporary cash creation. In the meantime the BOJ continues to print cash by means of bond purchases, compensating for the ECB and BOE’s shrinkage. The Chinese language credit score impulse has lately bottomed out in an indication of renewed credit score enlargement relative to the dimensions of the economic system.
Edited by Sheldon Reback.
[ad_2]