
[ad_1]
Blockchain expertise is a decentralized and distributed ledger that allows safe, clear, and immutable transactions. It operates by means of a community of computer systems that validate and document every transaction in a sequence of blocks, that are linked and encrypted to type a series. This expertise has turn into more and more standard lately, with the rise of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Nevertheless, blockchain expertise is greater than only a digital forex. It has a number of layers that allow its performance and efficiency. Understanding these layers is crucial for companies and buyers who need to leverage blockchain expertise for his or her operations or investments.
The Layers of Blockchain
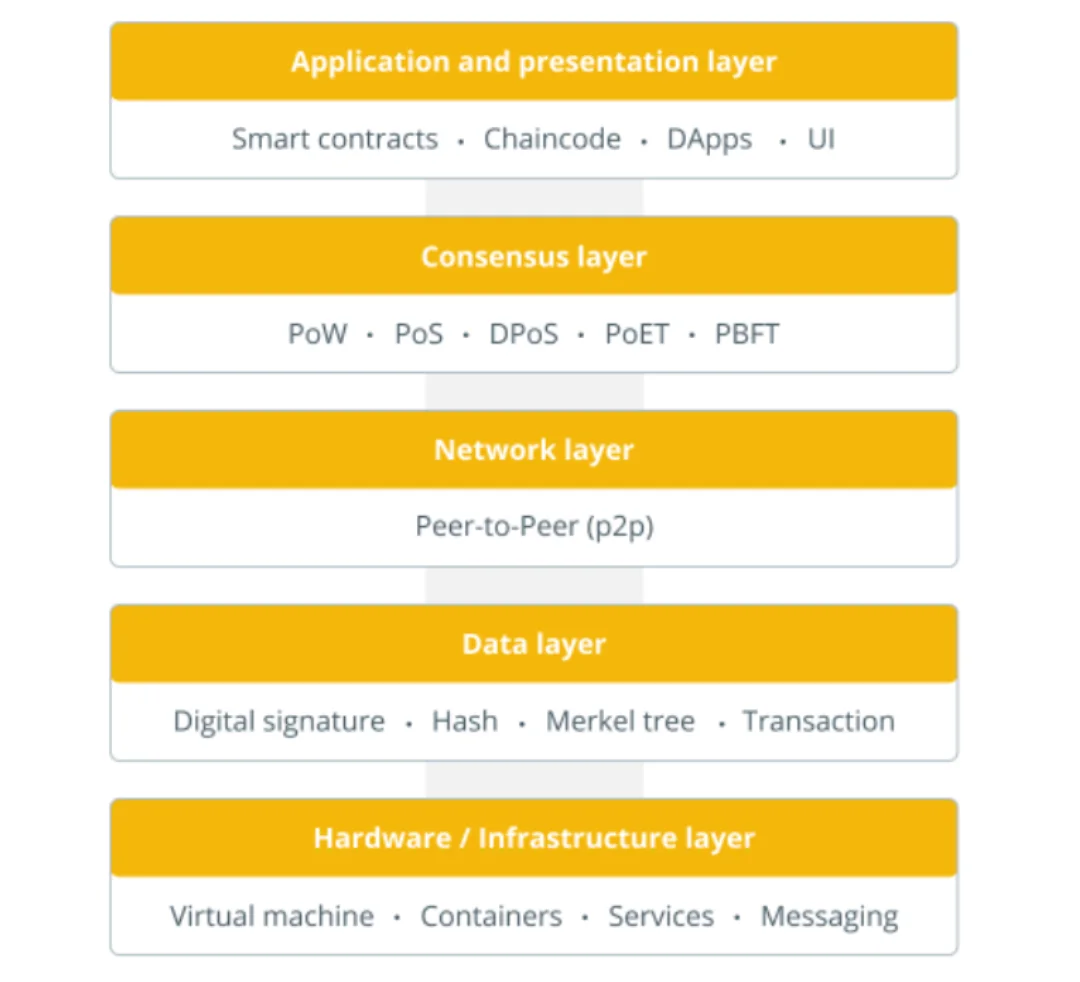
A typical blockchain system consists of a number of layers that work collectively to make sure the integrity and effectivity of transactions. These layers embody:
- Community Layer: This layer contains the bodily community of computer systems and nodes that talk with one another to type the blockchain community. It’s chargeable for connecting nodes, propagating transactions, and distributing information throughout the community.
- Consensus Layer: This layer ensures that every one nodes within the community agree on the validity of every transaction. It depends on a consensus mechanism, equivalent to Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain.
- Knowledge Layer: This layer shops all transaction information in a safe and immutable method. It contains the transaction ledger, which comprises all of the transactions within the blockchain, and the state database, which shops the present state of the blockchain.
- Utility Layer: This layer contains the good contracts, decentralized functions (dApps), and different software program that run on high of the blockchain community. It allows builders to construct new functions and companies that leverage the blockchain’s safety and transparency.
- {Hardware} Layer: This layer contains the bodily units, equivalent to computer systems and servers, that assist the blockchain community. It contains the {hardware} infrastructure, equivalent to mining tools, that’s used to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain.
Every layer within the blockchain system performs a crucial position in making certain the safety, transparency, and effectivity of transactions. Within the following sections, we’ll discover every layer in additional element and its significance for blockchain expertise.
The Significance of Blockchain Scalability
One of many greatest challenges going through blockchain expertise is scalability. As extra customers and transactions are added to the blockchain community, the system turns into slower and fewer environment friendly. It’s because the present blockchain structure can not assist the elevated demand for transaction processing.
To handle this situation, a number of options have been proposed, together with:
- Layer 1 vs. Layer 2 Blockchain: Layer 1 refers back to the base layer of the blockchain, the place all transactions are recorded and validated. Layer 2 refers to a secondary layer constructed on high of Layer 1 that may deal with extra transactions and enhance the blockchain’s scalability. Layer 2 options embody sidechains, state channels, and cost channels.
- Consensus Mechanism: The consensus mechanism utilized by the blockchain community may have an effect on its scalability. Proof of Work (PoW) is probably the most extensively used consensus mechanism in blockchain, however it’s gradual and energy-intensive. Proof of Stake (PoS) is a extra environment friendly consensus mechanism that may enhance blockchain scalability.
- Blockchain Structure: The blockchain structure may have an effect on its scalability. A sharded blockchain structure, for instance, can divide the blockchain community into smaller teams of nodes, every chargeable for processing a subset of transactions. This will enhance the blockchain’s scalability by lowering the load on every node.
- Distributed Ledger Know-how: Distributed ledger expertise (DLT) is a kind of blockchain expertise that may enhance scalability by enabling a number of nodes to course of transactions concurrently. This will enhance the velocity and effectivity of transaction processing, making the blockchain extra scalable.
The Six Layers of Blockchain
Along with the 5 layers described earlier, some blockchain specialists have proposed a further layer, Layer 0, which refers back to the underlying protocols and requirements that govern the blockchain community. This layer contains protocols equivalent to TCP/IP, HTTP, and SSL, which allow communication and safety on the blockchain community.
The six layers of blockchain are:
- Layer 0: The underlying protocols and requirements that govern the blockchain community.
- Layer 1: The community layer, which incorporates the bodily community of computer systems and nodes that talk with one another to type the blockchain community.
- Layer 2: The consensus layer, which ensures that every one nodes within the community agree on the validity of every transaction.
- Layer 3: The info layer, which shops all transaction information in a safe and immutable method.
- Layer 4: The applying layer, which incorporates the good contracts, dApps, and different software program that run on high of the blockchain community.
- Layer 5: The person layer, which incorporates the end-users who work together with the blockchain community by means of wallets, browsers, and different functions.
Conclusion
Blockchain expertise has the potential to revolutionize industries and rework the best way we conduct transactions. Understanding its layers and scalability is crucial for companies and buyers who need to leverage this expertise’s advantages. By addressing the scalability situation and bettering the blockchain structure, we will unlock its full potential and create a safer, clear, and environment friendly digital financial system.
[ad_2]